Cryptocurrency has moved from a niche experiment to a mainstream conversation, influencing how value is stored, transferred, and programmed on the internet. Whether you first heard about it through Bitcoin, a friend earning yield in DeFi, an artist selling NFTs, or a business accepting digital assets, the idea is the same: money and ownership recorded on a blockchain that anyone can audit. Yet understanding cryptocurrency deeply requires more than headlines. You need to know what problems it tries to solve, how the technology works under the hood, how to use it safely, and when it may or may not make sense for you.
This comprehensive guide demystifies cryptocurrency in practical, human terms. You will learn the fundamentals of smart contracts, wallets, and private keys; the difference between proof of work and proof of stake; where stablecoins fit; how to evaluate projects; and what to expect from regulations, taxes, and real-world adoption. By the end, you will be equipped to navigate cryptocurrency with confidence—curious, cautious, and ultimately capable of making informed decisions.
What Is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a form of digital currency secured by cryptography and recorded on decentralized networks called blockchains. Instead of relying on a bank to keep a ledger of who owns what, a blockchain distributes this ledger across many independent computers. Every participant can verify transactions, making the system transparent and resilient.
In practice, cryptocurrency can behave like money, like a programmable database, or like a new substrate for digital ownership. Bitcoin aims to be hard money with a fixed supply and predictable issuance. Ethereum extends the concept with smart contracts, enabling developers to create applications that run exactly as written, from lending protocols to gaming economies. Beyond those, thousands of tokens serve different purposes, from governance to access to utility within software platforms.
How Blockchain Works
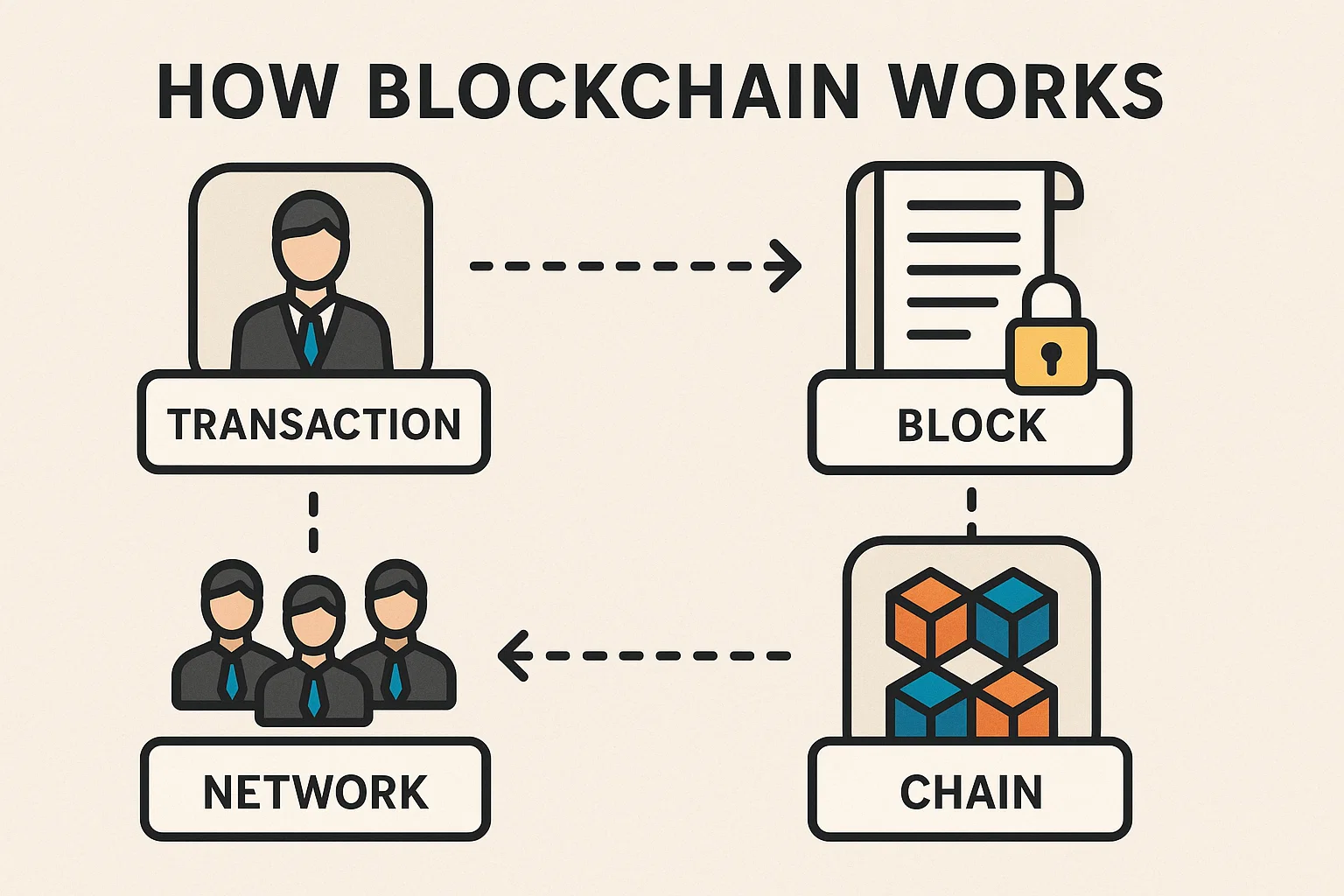
A blockchain is a chain of data blocks, each referencing the previous one in a way that makes tampering extremely difficult. Transactions are grouped into blocks, validated, and appended to the chain by network participants following a consensus mechanism. Because every node holds a copy of the blockchain, it’s nearly impossible for a single bad actor to alter history without controlling the majority of the network.
Two dominant consensus methods secure public blockchains today. Proof of work requires miners to expend computational energy to propose new blocks, aligning economic cost with network security. Proof of stake requires validators to lock up tokens (staking) and risk losing them if they behave dishonestly, aligning incentives with honesty and energy efficiency. Each model has trade-offs, but both aim to secure the ledger and maintain the integrity of cryptocurrency transactions.
The Role of Tokens and Coins
Not all tokens are the same. A coin like Bitcoin or ETH operates as the native asset of its network, paying fees and rewarding validators. Tokens built on top of networks, such as ERC-20 tokens on Ethereum, can represent virtually anything: governance rights, utility within an application, or claims on protocol cash flows. Some tokens are pegged to external assets, creating stablecoins like USDC or USDT, which attempt to maintain a one-to-one value with the U.S. dollar.
Understanding token design is crucial when evaluating a cryptocurrency. You should look at supply schedules, issuance rules, utility, and who controls upgrades. A well-designed token aligns with the long-term health of its network and community rather than enriching only insiders.
Wallets, Keys, and How to Hold Cryptocurrency Safely
Owning cryptocurrency means controlling the private keys that authorize transactions. A wallet is simply software or hardware that stores and manages those keys. There are two broad classes of wallets. A custodial wallet is managed by a third party—often an exchange—that holds keys on your behalf. This is convenient but requires trust. A non-custodial wallet gives you full control; you keep your keys on a device or a hardware wallet, and only you can move your funds.
Security is paramount. You should write down your seed phrase offline, enable two-factor authentication, and maintain strict hygiene against phishing. Many users combine approaches: long-term holdings in a hardware wallet, smaller amounts in a mobile wallet for spending, and temporary balances on an exchange for trading. If you lose your seed phrase and device for a non-custodial wallet, there is no customer support to recover funds. That finality is both the strength and the risk of cryptocurrency self-custody.
Transactions, Fees, and Networks
When you send a cryptocurrency transaction, you broadcast a signed message to the network. Validators include it in a block and confirm it probabilistically or finality-wise, depending on the chain. Costs vary. On some networks, gas fees fluctuate with demand; on others, fees are near zero due to higher throughput or different designs. Layer-2 systems such as optimistic rollups and zk-rollups bundle many transactions off-chain and settle them on a base layer, reducing costs while preserving security.
Choosing a network involves trade-offs between decentralization, speed, and cost. Ethereum prioritizes security and composability; Solana aims for high throughput; Bitcoin focuses on simplicity and resilience; other chains target niche use cases. Interoperability protocols and cross-chain bridges help assets move between ecosystems, though bridges introduce additional risk vectors.
Use Cases Beyond Speculation
While prices get headlines, cryptocurrency’s relevance grows with utility. The clearest examples are payments, savings in unstable economies, and programmable finance.
Payments and Remittances
For cross-border transfers, stablecoins offer near-instant settlement and global reach without banking friction. A merchant can hold stablecoins to avoid volatility and convert to local currency when needed. For migrant workers, sending value home through a wallet can be faster and cheaper than traditional remittance services, especially in regions with limited bank access.
Savings and Financial Access
In countries facing high inflation or capital controls, people turn to Bitcoin or stablecoins as alternative stores of value. While not risk-free, cryptocurrency can serve as an accessible on-ramp to the global economy, especially when paired with user-friendly mobile wallets.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized finance uses smart contracts to automate lending, trading, and asset management without intermediaries. Users can swap tokens on automated market makers, provide liquidity to earn fees, borrow against collateral, or participate in yield strategies. DeFi is open, programmable, and transparent—every position and interest rate is visible on-chain. Its risks, however, include contract bugs, oracle failures, and governance attacks, so careful due diligence is essential.
Digital Ownership and NFTs
NFTs represent unique digital items—art, in-game assets, tickets, or identities. The technology allows creators to encode royalties, marketplaces to verify provenance, and communities to coordinate membership. While hype cycles come and go, the core idea—verifiable ownership of scarce digital goods—has broad applications beyond art, including supply chains, education credentials, and real estate titles.
Investing in Cryptocurrency: Frameworks and Caution
Investing in cryptocurrency requires a mindset that blends technology analysis with portfolio discipline. Begin by determining your risk tolerance and investment horizon. Cryptocurrency markets can move sharply; allocate only what you can withstand in downside scenarios.
A thoughtful approach starts with understanding narratives and traction. Ask what problem a project solves, how large the addressable market is, and whether users genuinely benefit from decentralization. Evaluate network effects, developer activity, and protocol revenues where applicable. Consider token distribution: heavy insider allocations with short vesting schedules can suppress the price for a long time. Scrutinize documentation, audits, and the pace of upgrades on public repositories.
Diversification helps manage risk. Many investors hold a core position in major assets like Bitcoin and Ethereum, then explore smaller allocations to promising DeFi protocols, layer-2 networks, or infrastructure tokens. Dollar-cost averaging can reduce timing risk. Finally, plan your exit strategy. Set rules for taking profits, rebalancing, and cutting losers, and write them down to counteract emotions during volatility.
Volatility and Market Cycles
Cryptocurrency markets often follow boom-and-bust cycles. New technology sparks excitement; prices surge, then cool as reality catches up. Catalysts such as network upgrades, macroeconomic shifts, or regulatory clarity can influence these cycles. Volatility is not merely noise; it is a reflection of price discovery in an emerging asset class with 24/7 trading and global participation.
To navigate cycles, focus on fundamentals and time horizons. Consider on-chain indicators like active addresses, fee revenue, and developer commits. Monitor liquidity across exchanges and on-chain lending markets. Understand leverage dynamics: when funding rates or collateral ratios stretch, a small move can force liquidations and cascade. Risk management—position sizing, stop losses, and secure custody—matters as much as asset selection.
Regulation, Taxes, and Compliance
Cryptocurrency touches traditional financial systems and therefore attracts regulatory scrutiny. Many jurisdictions require exchanges to follow KYC and AML rules. Securities regulators may classify certain tokens as investment contracts depending on how they are offered and marketed. Payment regulators examine stablecoins, particularly their reserves and redemption mechanisms. Central banks are exploring CBDCs—central bank digital currencies—to modernize payment rails while maintaining monetary oversight.
For individuals and businesses, taxes are a practical concern. In many countries, selling, swapping, or spending cryptocurrency is a taxable event that triggers capital gains or income tax. Keeping records is crucial. Track acquisition dates, cost basis, and proceeds for every transaction, including staking rewards, mining income, and airdrops. Specialized software can help reconcile on-chain activity with fiat reporting.
Security Threats and How to Avoid Them
The transparency of public blockchains makes them powerful—and also a magnet for attackers. Common threats include phishing, fake support agents, malicious browser extensions, and smart contract exploits. Bridges connecting chains have been frequent targets. Even reputable DeFi protocols can suffer from logic bugs or governance attacks.
You can dramatically reduce risk with a layered approach. Use a hardware wallet for long-term storage and sign only what you understand. Confirm contract addresses from official sources, not social media links. Split funds across separate wallets: one for daily use, one for DeFi experimentation, and one cold wallet that never connects to a browser. Keep operating systems updated and consider a dedicated device for crypto activity. Finally, accept that perfect security does not exist; the goal is to be cautious enough that opportunistic threats move on.
How to Research a New Cryptocurrency
Due diligence is both an art and a checklist. Start with the team and community. Public builders, clear documentation, and active forums are positive signs. Read the whitepaper or litepaper, but do not stop there. Explore the code repositories to gauge cadence and quality of development. Review audits, but remember they are not guarantees. Assess tokenomics: supply caps, emission schedules, burn mechanisms, and actual demand for the token’s utility.
Next, test the product. If it is a wallet, try small transactions. If it is a DeFi app, deposit tiny amounts, observing UX, fees, and fail-safes. Check on-chain dashboards for usage statistics and growth trends. Compare competitors honestly; sometimes the best decision is to pass. A disciplined “no” saves more capital than a lucky “yes.”
Stablecoins: Why They Matter
Stablecoins bridge traditional money and cryptocurrency, enabling predictable pricing for on-chain commerce and hedging. Fully reserved stablecoins hold short-term treasuries and cash equivalents, offering transparent attestations. Algorithmic stablecoins attempt to hold the peg through incentives and market dynamics; some have succeeded in specific conditions, while others have failed spectacularly. When you use a stablecoin, investigate redeemability, transparency, and counterparty risk. Ask who issues it, who audits it, and how quickly reserves can be converted to cash in stress.
The Environmental Question
Critics often point to energy usage. Proof of work consumes substantial electricity by design, translating energy into security. Supporters argue that miners increasingly use renewable or stranded energy, stabilizing grids and monetizing waste gas. Proof of stake dramatically reduces energy consumption by replacing computation with economic bonds. The broader point is to understand the trade-offs: security models, decentralization, and ecological impact are intertwined, and different networks are experimenting with different balances.
Business Adoption and Enterprise Use
Businesses adopt cryptocurrency for varied reasons: to accept digital payments, to settle cross-border invoices faster, to hold Bitcoin as a treasury asset, or to build new products on smart contracts. Enterprise blockchains may opt for permissioned networks to meet compliance requirements, while startups often favor public chains for composability and ecosystem effects. For CFOs, key considerations include custody solutions, accounting standards, volatility management, and regulatory obligations. For product teams, the question is where blockchain adds real user value rather than buzz.
The Future of Cryptocurrency
The long-term arc points to more utility and smoother UX. Layer-2 scaling will continue to lower fees and improve throughput. Better wallet abstractions will hide private keys behind secure recovery methods, making onboarding feel like a modern app rather than a command-line tool. Decentralized identity could enable reputation and credit history without sacrificing privacy. Cross-chain communication will improve, reducing the need for risky bridges. CBDCs and regulated stablecoins may coexist, with clear segregation of roles: public blockchains for open innovation, sovereign money for state functions.
Institutional participation will deepen liquidity and standards. Retail users will interact with cryptocurrency without always realizing it, as games, social apps, and payment platforms integrate on-chain features in the background. As with the early web, the most transformative applications may be the ones we cannot predict yet.
Common Myths About Cryptocurrency
One myth is that cryptocurrency is only for criminals. In reality, the traceability of blockchains makes illicit use difficult to hide, and analytics firms help law enforcement track flows. Another myth is that all tokens are scams. While scams exist, many legitimate projects are open source, audited, and governed transparently. A third myth is that cryptocurrency is too complex for everyday use. The learning curve can indeed be steep, but abstraction layers and consumer-grade wallets are improving quickly.
Step-by-Step: Your First Transaction
If you want to try cryptocurrency safely, start small. Choose a reputable exchange for onboarding, complete KYC, and fund your account. Buy a modest amount of Bitcoin or ETH to learn mechanics rather than to get rich. Transfer a tiny amount to a non-custodial wallet you control. Practice backing up your seed phrase, verifying addresses, and exploring transaction explorers to see your transfer on the blockchain. When you are comfortable, you can explore DeFi or NFT marketplaces—again, with tiny sums at first.
Each small step demystifies the process and builds responsible habits. You will learn how networks confirm transactions, how fees are calculated, and how to read on-chain data. This hands-on approach teaches more than weeks of reading, while limiting downside.
Ethical and Social Considerations

Cryptocurrency raises questions about inclusivity, privacy, and power structures. Open protocols lower barriers to entry; anyone with a phone can create a wallet and transact. Yet wealth concentration and speculative mania can exacerbate inequality. Builders need to design with fairness in mind: transparent launches, community allocations, and tools that protect users from predatory schemes. Privacy-preserving technologies should be used to shield innocent users without enabling abuse. Thoughtful governance—on-chain voting, DAO participation, and community stewardship—helps align incentives across stakeholders.
See More: Best Cryptocurrency Investment Strategies for Beginners Complete 2025 Guide
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency is more than a price chart; it is a new way to transmit value, encode rules, and coordinate communities on the internet. By understanding blockchains, smart contracts, wallets, and the economics of tokens, you can evaluate opportunities and risks with clear eyes. Approach the space with curiosity and discipline. Secure your private keys, diversify prudently, document your taxes, and never risk funds you cannot afford to lose. If you focus on real utility—payments, savings, programmable finance, and digital ownership—you will see why cryptocurrency continues to attract builders, investors, and everyday users worldwide.
FAQs
Q: What exactly gives cryptocurrency its value?
Value comes from utility, scarcity, and network effects. For Bitcoin, predictable supply and strong security underpin its role as digital gold. For Ethereum and similar platforms, demand for smart contracts and on-chain applications creates usage that drives fees and token demand. Ultimately, markets price in adoption, security, and credible neutrality.
Q: Is cryptocurrency legal where I live?
Legality varies by jurisdiction. Many countries allow ownership and trading while enforcing KYC/AML rules on exchanges. Some restrict certain activities like derivatives. Before using DeFi or launching a token, review local regulations and, when necessary, seek professional advice.
Q: How do I keep my funds safe from hacks and scams?
Use a hardware wallet for long-term storage, protect your seed phrase offline, enable two-factor authentication, and verify URLs and contract addresses from official sources. Start with small transactions and segment wallets for different purposes. Assume unsolicited help is malicious, especially on social platforms.
Q: Are stablecoins really stable?
Peg stability depends on design and reserves. Fiat-backed stablecoins rely on high-quality, short-duration assets and transparent attestations. Algorithmic approaches depend on market incentives and can fail under stress. Evaluate redeemability, transparency, and counterparty risk before relying on any stablecoin.
Q: Do I have to pay taxes when I use cryptocurrency?
In many jurisdictions, selling, swapping, or spending cryptocurrency triggers taxes on gains or income, including staking rewards and mining proceeds. Keep detailed records of cost basis and transaction history, and consider using specialized software or professional tax support to stay compliant.

